DeFi is short for “Decentralized Finance”. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging concept that is revolutionizing the traditional finance sector. The need for an open, transparent, and secure financial system is the key driver behind the concept of decentralized finance.
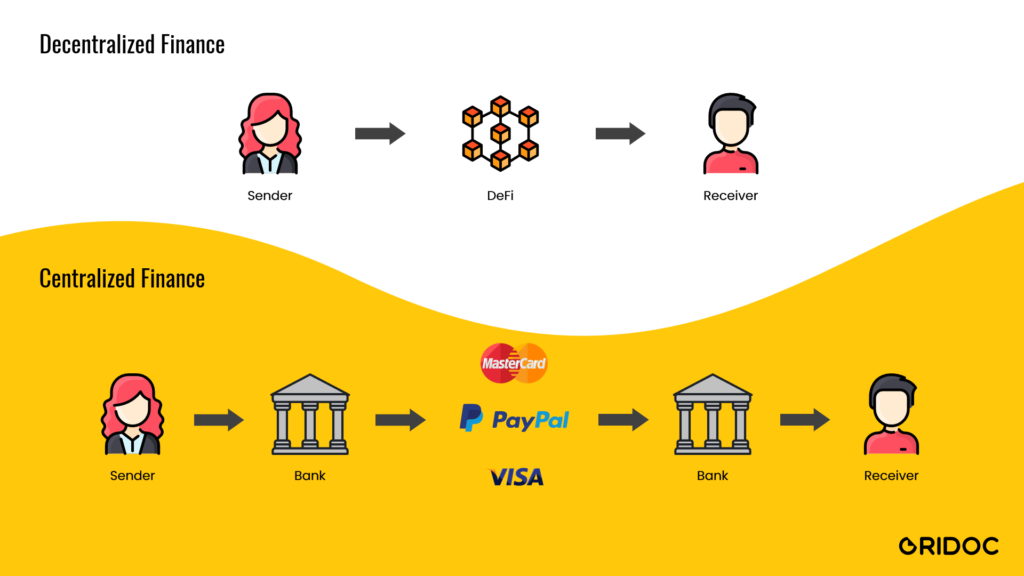
DeFi is making a new financial system that is transparent and doesn’t require trusting intermediaries like banks, central governing authorities. DeFi relies on cryptography, blockchain and smart contracts. DeFi is based on blockchain, the technology behind digital currencies, which allows several entities to hold a copy of a history of transactions, meaning it isn’t controlled by a single, central source. DeFi is distinct because it expands the use of blockchain from simple value transfer to more complex financial use cases.
1. Banking Services
Conventional payments processing requires documentation, insurance issuance, and validation and contracts. All of these steps are performed on sluggish legacy systems that reduce operational efficiency. Such delay result is high receivables and lowered profitability. By digitalizing and implementing DeFi solutions, users can reduce dependency on several IT solutions. Blockchain can transparently offer contract management and, at the same time, handle payments in real-time. Cryptocurrency such as Ripple makes it possible for people to send and receive money without having to worry about bans or restrictions.
2. Lending and Borrowing
Decentralized applications (DApps) that allow users to either lend their digital assets out to other users to earn interest or borrow digital assets from other users by paying interest on top. For example, Aave is an Open Source and Non-Custodial protocol to earn interest on deposits & borrow assets.
3. Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges are hassle free of sign-ups. In most cases, there’s no depositing or withdrawing crypto. The trade happens directly between two users’ wallets. For example, Mdex is an automatic market-making decentralized exchange based on the concept of fund pools.
4. Decentralized Insurance
DeFi platforms can offer similar insurance against practically any unfortunate or unforeseen event. Unlike with traditional insurers, decentralized insurance allows a pool of investors (known as underwriters) to share the risk among themselves in return for the insurance premium. Cover Protocol allows DeFi users to buy protection against smart contract risk.
5. Staking
Staking helps the users to participate in the network governance of Proof-of-Stake (POS) blockchains, by either delegating digital assets to a validator node or by simply holding these digital assets in a compatible wallet. When you help assets, Users can earn rewards by helping to secure the blockchain. Some of the more popular stackable assets include Tezos (XTZ), Tron (TRX), and Cardano (ADA).
6. Yield Farming
Yield farming (also known as liquidity mining) is one of the more recent DeFi use-cases. This is the practice of locking up digital assets in return for rewards which are usually automatically delivered by a smart contract.
The ability to provide uncensored access to global financial services is one of the reasons why decentralized finance will continue to stand out from traditional finance. The idea of building censorship-resistant products in the financial sector will continue to fuel decentralized finance popularity.
At oridoc, we are excited about the future of DeFi in different industries and our personal lives. If you want to learn more about DeFi use cases, and want to explore how to integrate DeFi for your business, just drop a line via our contact form and we will guide you through over a cup of coffee.







0 Comments